Page 89 - 理化检验-物理分册2021年第十二期
P. 89
陈亮平, 等: 汽轮机高温螺栓断裂原因
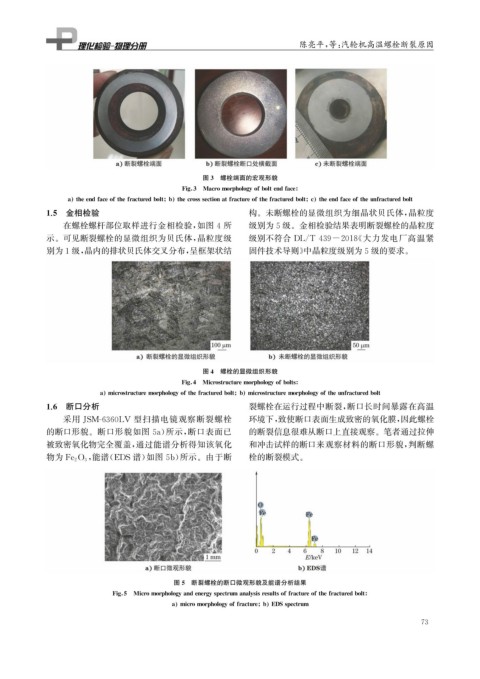
图3 螺栓端面的宏观形貌
Fi g 3 Macromor p holo gy ofboltendface
a theendfaceofthefracturedbolt b thecrosssectionatfractureofthefracturedbolt c theendfaceoftheunfracturedbolt
1.5 金相检验 构。未断螺栓的显微组织为细晶状贝氏体, 晶粒度
在螺栓螺杆部位取样进行金相检验, 如图4所 级别为5级。金相检验结果表明断裂螺栓的晶粒度
示。可见断裂螺栓的显微组织为贝氏体, 晶粒度级 级别不符合 DL / T439-2018 《 大力发电厂高温紧
别为1级, 晶内的排状贝氏体交叉分布, 呈框架状结 固件技术导则》 中晶粒度级别为5级的要求。
图4 螺栓的显微组织形貌
Fi g 4 Microstructuremor p holo gy ofbolts
a microstructuremor p holo gy ofthefracturedbolt b microstructuremor p holo gy oftheunfracturedbolt
1.6 断口分析 裂螺栓在运行过程中断裂, 断口长时间暴露在高温
采用 JSM-6360LV 型扫描电镜观察断裂螺栓 环境下, 致使断口表面生成致密的氧化膜, 因此螺栓
的断口形貌。断口形貌如图 5a ) 所示, 断口表面已 的断裂信息很难从断口上直接观察。笔者通过拉伸
被致密氧化物完全覆盖, 通过能谱分析得知该氧化 和冲击试样的断口来观察材料的断口形貌, 判断螺
, 能谱( EDS 谱) 如图 5b ) 所示。由于断
物为 Fe 2O 3 栓的断裂模式。
图5 断裂螺栓的断口微观形貌及能谱分析结果
Fi g 5 Micromor p holo gy andener gy s p ectrumanal y sisresultsoffractureofthefracturedbolt
a micromor p holo gy offracture b EDSs p ectrum
7 3